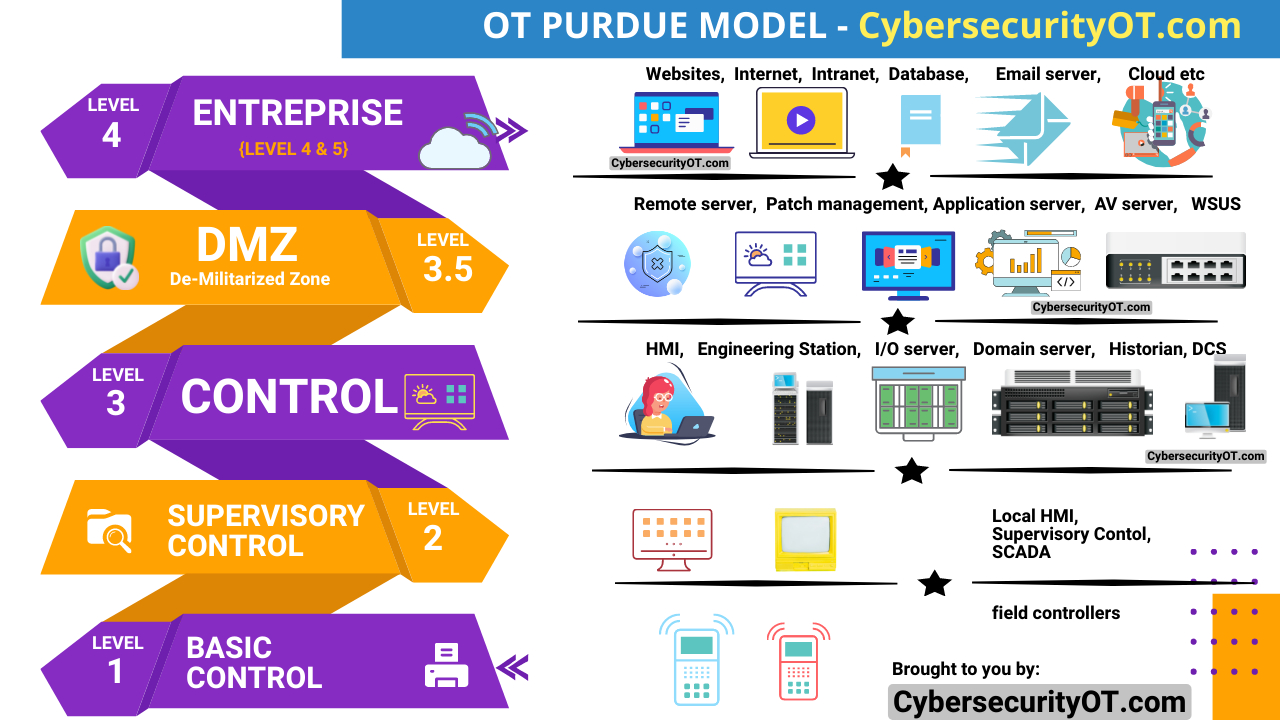
Data diddling and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks are two distinct types of cyber attacks, although they both involve manipulation of data. Here’s a differentiation between the two:
Data Diddling:
- Definition: Data diddling involves the unauthorized alteration of data at any stage of its processing, transmission, or storage. Read More about data diddling.
- Objective: The primary goal of data diddling is to manipulate data to achieve malicious outcomes, such as disrupting operations, stealing information, or covering up other attacks.
- Methods: Attackers may tamper with data directly on a storage device, during transmission over a network, or while it’s being processed by an application or system.
- Example: Modifying financial transaction records in a database to siphon funds into the attacker’s account would be considered a data diddling attack.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack:
- Definition: A man-in-the-middle attack occurs when an attacker intercepts and possibly alters communications between two parties without their knowledge or consent.
- Objective: The main objective of an MITM attack is to eavesdrop on sensitive information exchanged between the two parties or to manipulate the communication for malicious purposes.
- Methods: Attackers position themselves between the communicating parties, intercepting and sometimes modifying data packets as they pass through. This can be achieved through techniques such as ARP spoofing, DNS spoofing, or SSL stripping.
- Example: Intercepting unencrypted login credentials exchanged between a user and a web server, allowing the attacker to access the user’s account.
In summary, while both data diddling and man-in-the-middle attacks involve manipulation of data, they differ in their objectives, methods, and the stage at which the data is manipulated. Data diddling focuses on altering data itself to achieve malicious outcomes, whereas MITM attacks involve intercepting and potentially modifying data during communication between two parties.