What is Data diddling?
Data diddling is a form of cyber attack where an attacker manipulates data during its input, processing, transmission, or output to cause disruptions, steal information, or achieve other malicious objectives. This type of attack is particularly concerning in manufacturing and Industrial Control Systems (ICS) environments, where the integrity of data is critical for safe and efficient operations.
How can Data diddling affect Operational Technology / ICS / CPS environments?
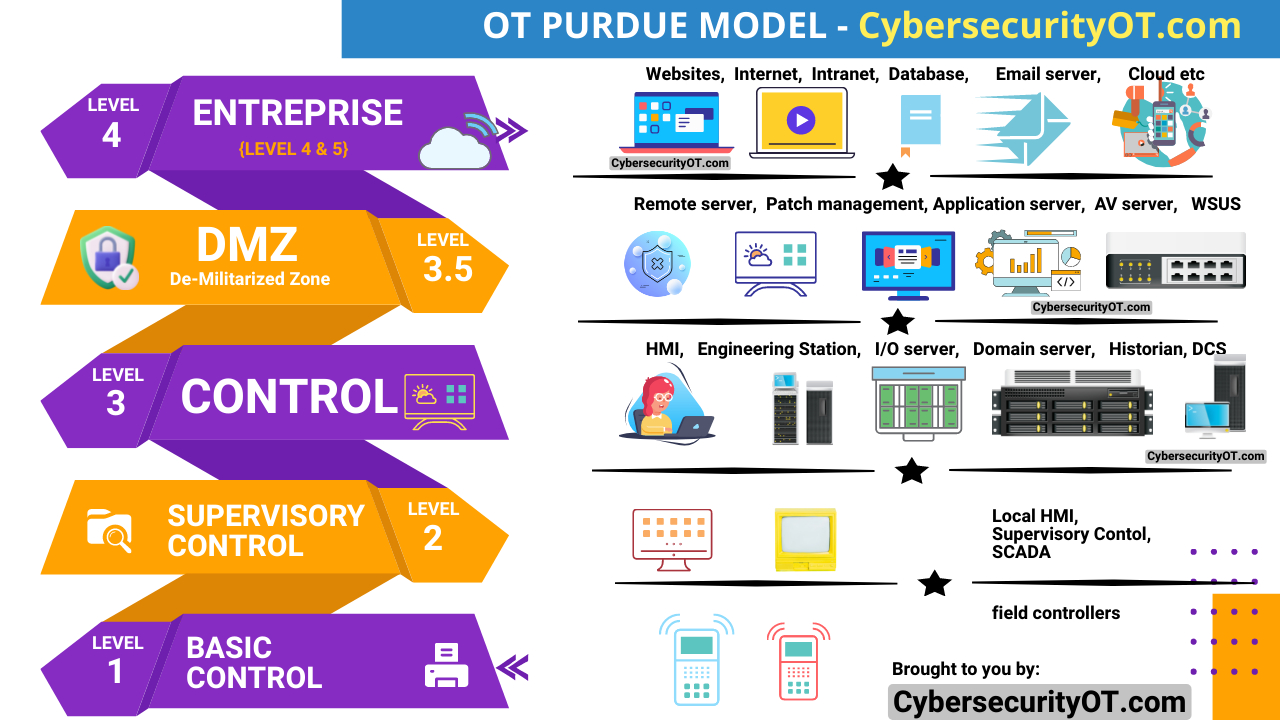
One of the biggest challenges in an Operational Environment is the use of legacy protocols like Modbus. With legacy computers on ground, it becomes more easy to tamper such systems. The issue is more prominent in some critical infrastructure sites where replacing older systems is not practical.
In addition, a lot of information is stored unsecured within the OT environment – for e.g. many automation vendor do not save logfiles securely. Backup data are stored on local machines or on hard drives which could be accessed by multiple people who have access to the site.
Since availability is important in a production environment, there is little or no control implemented to validate data flow. However, “restricted data flow”, which is one of the foundational requirements as per IEC 62443 can be utilized to enhance security.
How can an data diddling impact manufacturing/ICS environment?
In manufacturing/ICS environments, data diddling can be used by attackers to:
- Manipulate Process Control: Attackers may tamper with data related to process control systems, causing machinery to malfunction or produce defective products.
- Sabotage Production: By altering production schedules or quality control data, attackers can disrupt production processes, leading to financial losses or safety hazards.
- Steal Intellectual Property: Manipulating design or production data can allow attackers to steal intellectual property or trade secrets, impacting the competitiveness of the organization.
- Cover Up Other Attacks: Attackers might manipulate data to cover up their tracks during other forms of cyber attacks, such as ransomware or espionage.
What are the key methods to mitigate this risk especially in an ICS/OT environment?
To mitigate the risk of data diddling, especially in ICS/OT environments, organizations can implement several key methods:
- Access Control: Limit access to critical systems and data to authorized personnel only. Implement strong authentication mechanisms and role-based access controls to prevent unauthorized manipulation of data.
- Data Integrity Checks: Implement data integrity checks at various stages of data processing to detect any unauthorized alterations. This includes checksums, digital signatures, and other cryptographic methods to verify the integrity of data.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting the network into separate zones with controlled communication flows can prevent attackers from easily accessing and manipulating critical data.
- Anomaly Detection: Deploy anomaly detection systems that can identify unusual patterns or behaviors in data traffic, indicating potential data manipulation attempts.
- Regular Auditing and Monitoring: Conduct regular audits of system configurations, data logs, and user activities to detect any suspicious changes or unauthorized access. Continuous monitoring of network traffic and system activities can also help identify data diddling attempts in real-time.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees about the risks of data manipulation and the importance of following security protocols. Training programs should include guidance on recognizing phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other common attack vectors.
- Vendor Security: Ensure that third-party vendors and suppliers adhere to strict security standards and practices, especially if they have access to critical systems or data.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan specifically tailored for data manipulation incidents. This plan should include procedures for containing the attack, restoring data integrity, and communicating with stakeholders.
By implementing these measures, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data diddling attacks in manufacturing and ICS environments, safeguarding critical systems and data from manipulation and exploitation by malicious actors.