Conducting a vulnerability assessment for an operational technology (OT) site is crucial for identifying and mitigating potential security risks. Here are general steps to help you in the process:
- Define Scope and Objectives:
- Clearly define the scope of the vulnerability assessment, including the assets and systems to be assessed.
- Identify the specific objectives of the assessment, such as identifying vulnerabilities, assessing the impact of potential exploits, and prioritizing remediation efforts.
- Asset Inventory:
- Create an inventory of all OT assets, including hardware, software, network devices, and other components.
- Document the purpose and criticality of each asset in the context of OT operations.
- Identify Threats and Vulnerabilities:
- Analyze potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to OT environments. Consider both technical and non-technical risks.
- Leverage threat intelligence sources to stay updated on current threats and vulnerabilities relevant to OT systems.
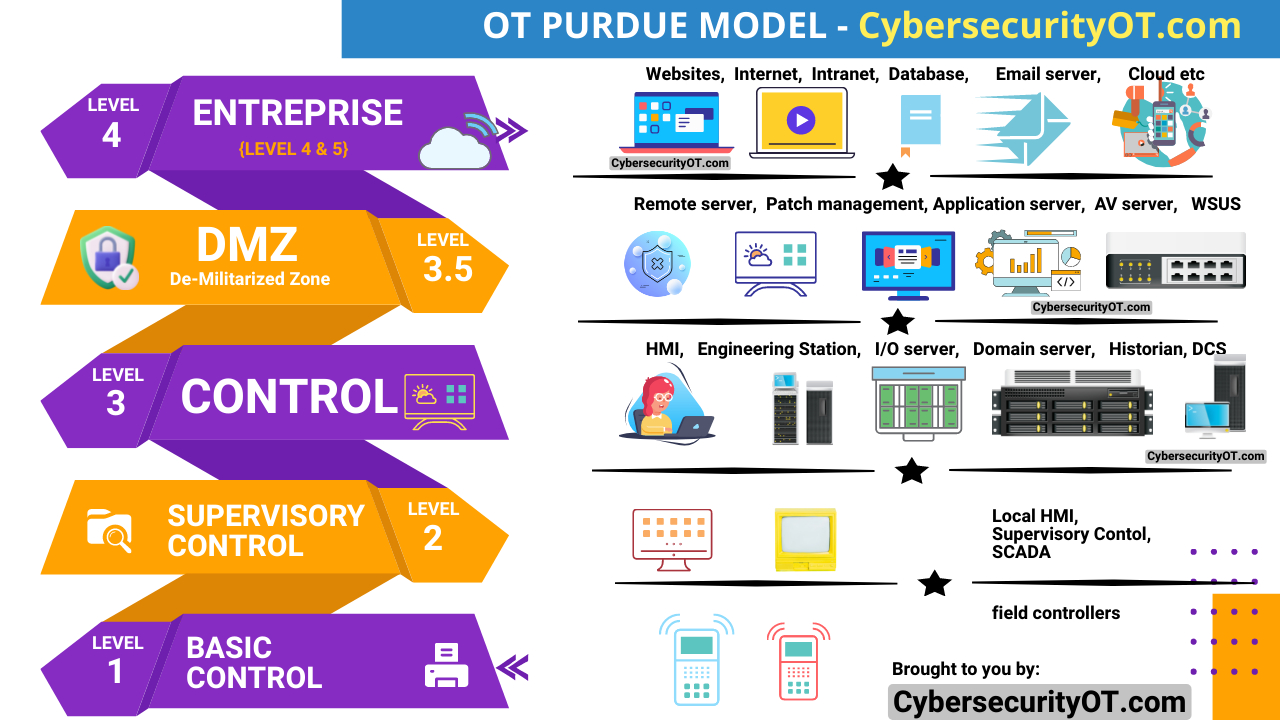
- Network Mapping:
- Map the network architecture of the OT environment, including communication paths and connections between devices.
- Identify entry points and potential pathways that could be exploited by attackers.
- Asset Vulnerability Assessment:
- Perform vulnerability scanning on all OT assets to identify known vulnerabilities.
- Use specialized tools designed for OT environments to ensure accurate results without disrupting critical processes.
- Risk Assessment:
- Evaluate the impact and likelihood of exploitation for each identified vulnerability.
- Assign risk levels to vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on operations and confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of OT assets.
- Prioritization:
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their risk level and potential impact on OT operations.
- Consider the ease of exploitation and the criticality of the affected systems when prioritizing remediation efforts.
- Penetration Testing (Optional):
- Conduct penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and identify potential weaknesses that automated scans might miss.
- Ensure that penetration testing is conducted by experienced professionals who understand OT environments.
- Documentation and Reporting:
- Document all findings, including vulnerabilities, risk assessments, and recommended remediation steps.
- Generate a comprehensive report that can be shared with stakeholders, including management and IT/OT personnel.
- Remediation and Mitigation:
- Develop a plan for remediation that addresses the identified vulnerabilities.
- Prioritize and implement security controls and countermeasures to mitigate risks.
- Continuous Monitoring:
- Implement continuous monitoring mechanisms to detect and respond to new vulnerabilities and threats as they emerge.
- Regularly reassess the security posture of the OT environment.
- Training and Awareness:
- Provide training and awareness programs for OT personnel to enhance their understanding of security best practices and the importance of maintaining a secure environment.
Remember that OT environments can be complex and may have unique challenges compared to traditional IT systems. It’s crucial to involve OT specialists, follow industry standards, and comply with relevant regulations throughout the vulnerability assessment process. Additionally, consider seeking assistance from experienced OT security professionals if needed.